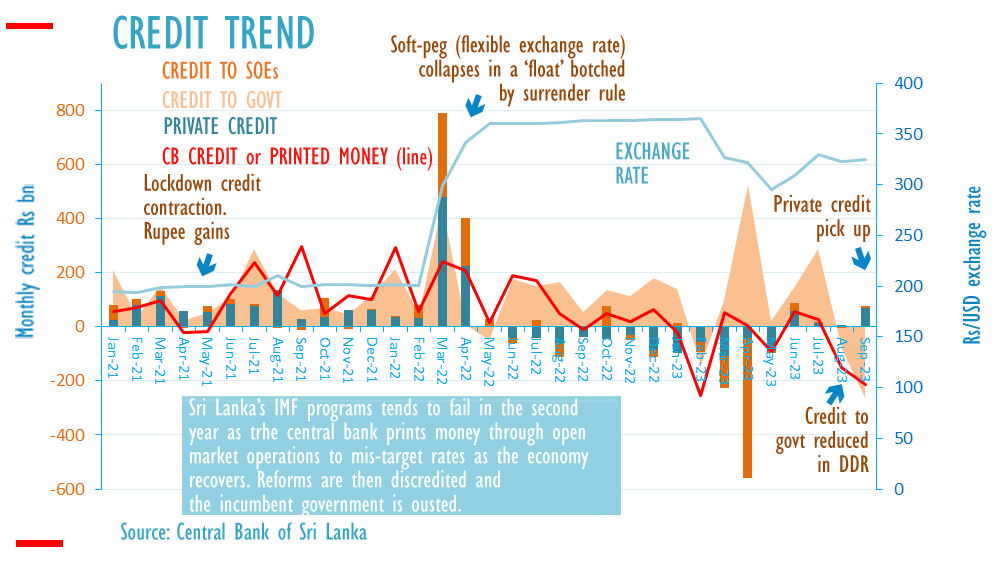
ECONOMYNEXT – Sri Lanka’s personal credit score expanded for the fourth straight month in September 2023, official knowledge confirmed, whereas authorities credit score contracted as a consequence of a home debt restructuring.
Retail credit score grew by 69.9 billion rupees in September, up from 5.5 billion rupees in August.
Sri Lanka’s personal credit score sometimes recovers about twelve to eighteen months after a profitable inventory alternate ends a stability of funds disaster brought on by bureaucratically determined rate of interest cuts.
In 2022, the BOP returned to a surplus in September after personal credit score contracted as a consequence of market rates of interest, however a confidence-boosting impact didn’t happen till March 2023, after the removing of a give up rule that pushed the foreign money down.
A profitable IPO places an finish to capital flight and likewise brings in cash, stopping additional will increase in rates of interest.
Nonetheless, after the foreign money disaster, rates of interest are typically excessive because of the destruction of actual capital and the necessity to construct up reserves (financing the deficit of the opposite US reserve foreign money international locations), regardless that the home price range deficit is below management.
In September, lending to the federal government by the banking system fell by 261 billion rupees as a consequence of central financial institution debt restructuring.
Any sale of debt held by the central financial institution to the personal sector (deflationary open market operations) additionally tends to scale back internet credit score to the federal government as outlined in Sri Lanka, making a stability of funds surplus.
Nonetheless, recovering personal credit score tends to place upward strain on rates of interest. The central financial institution has prior to now engaged in aggressive open market operations to chop rates of interest, triggering a second foreign money disaster and a depreciation of the rupee.
Below earlier IMF applications, the central financial institution was free to print cash primarily based on the declare that inflation is low, no matter the truth that it’s a reserve-accumulating central financial institution.
The foreign money then depreciates, inflicting power and meals costs to rise, the IMF’s reserve targets are missed, reforms are discredited, and the incumbent authorities is ousted, unraveling the reforms.
Central banks delicate to the IMF (so-called repeat offenders or Many Pleased Returns) are likely to print cash to stimulate progress (pursue potential output), thus denying financial stability to financial actors, together with the federal government.
Printing cash for progress (potential manufacturing) was legalized in a brand new financial regulation, supported by the IMF.
Nations with regressive IMF-style central banks are likely to have excessive nominal rates of interest, as a result of foreign money crises and stabilization applications are available fast succession and depreciation destroys capital and causes social unrest.
The IMF was initially created to halt depreciation, however after the second modification of its articles within the late Seventies, fast depreciations and defaults grew to become frequent within the Eighties and inflation and rates of interest between the IMF and non-IMF delicate international locations range extensively.
Sarcastically, essentially the most developed international locations of the Eighties, together with Britain and the US itself, which suffered from BOP issues as a consequence of mistargeted rates of interest to stimulate progress whereas pegged to the US greenback and gold , switched to 1 anchor regime. (Colombo/05 November 2023)